The shelf life of freeze-dried or highly dehydrated products can be determined by several methods. Here are some of the steps for determining the shelf life of these products:
- Identify the factors affecting product stability: these may include temperature, light, moisture, oxygen, and the amount of free water.
- Conduct stability studies: these studies are designed to monitor how the factors identified affect product stability over time.
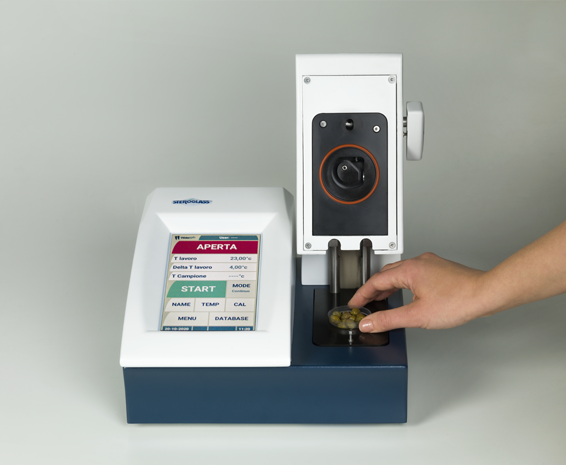
- Use a water activity meter: A water activity meter based on the dew point can be used to determine the amount of free water in the freeze-dried or highly dehydrated product, which is an indicator of product shelf life.
- Analyze results: the results of stability tests and free water measurement can be analyzed to determine the product’s shelf life.
- Take appropriate action: if the results indicate that the product shelf life is below acceptable levels, measures can be taken to improve the stability of the product, such as by changing storage conditions or improving the production process.
It is important to know that the shelf life of a freeze-dried or highly dehydrated product may vary depending on the specific product and the storage conditions. Therefore, tests must be conducted regularly to ensure that the product shelf life is constantly monitored and that the product is stored safely and reliably.
Why free water determines the shelf life of a product
Free water in a food or pharmaceutical product is the amount of water that is not chemically bound to the molecules in the product. This amount of water is free to interact with other chemicals and microorganisms, which can cause the product to deteriorate.
Free water (aw) is part of the total water in a given product (moisture). Knowing the moisture alone is not enough to understand the possible stability risks. Measuring water activity directly is essential for determining the shelf life of a product.
In the food and pharmaceutical industries, free water is an important factor for product quality and stability. A high amount of free water in a food can promote mold and bacteria growth, reducing the product’s shelf life. Similarly, free water in a pharmaceutical product can cause the active ingredient to deteriorate, reducing the efficacy of the product.

Freeze-dried and highly dehydrated products
Freeze-dried and highly dehydrated products contain very little water. These products are usually stored in areas with low humidity to preserve their stability and quality.
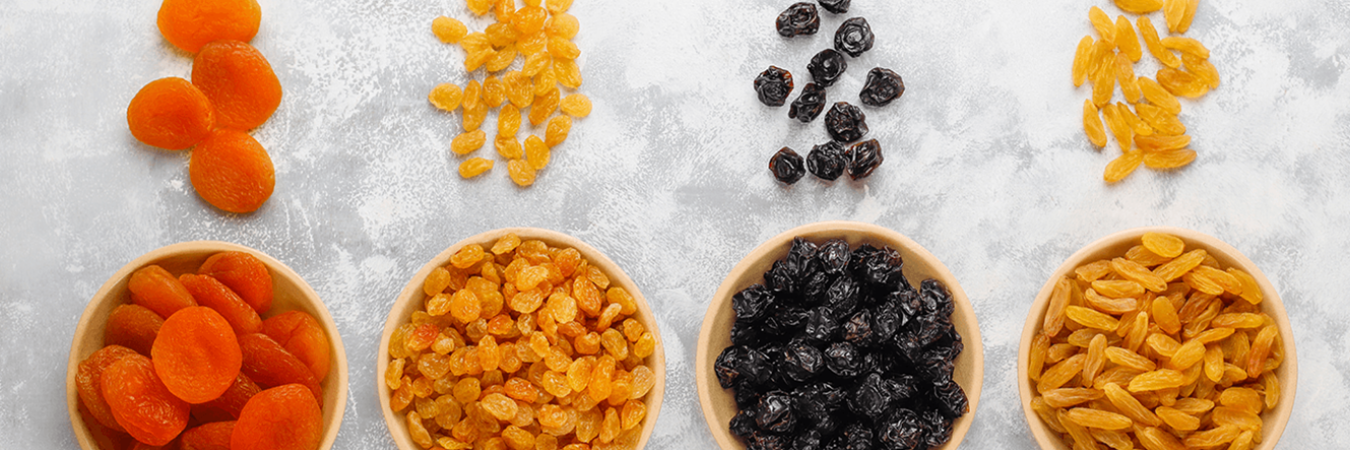
In the food industry, for example, freeze-dried and highly dehydrated foods include pasta, rice, dried fruit, dehydrated vegetables and powdered products such as milk and beverages.
Freeze-dried and highly dehydrated products such as tablets and capsules are also common in the pharmaceutical industry.
It is important to measure the amount of free water in freeze-dried and highly dehydrated products to determine their shelf life.
Dew point: the most reliable measurement method
The dew point method is the recommended method for measuring free water.
A water activity meter that uses dew point as a measurement method offers several advantages over other measurement methods. Some of these benefits include:
- Accuracy: Dew point is a very accurate measure of the amount of water a product contains. This is because the dew point is directly correlated to the real quantity of water that is naturally released by a product and stabilizes inside the analysis cell.
- Speed: The dew point works very quickly, making water activity meters that use this technology ideal for industrial applications that require fast, reliable results.
- Wide range of applications: The dew point is a universal measure of water quantity, which means that this type of meter can be used for a great variety of products, including those containing gases or are vaporized or in solution.
- Safety: The dew point is a non-invasive measurement of the amount of water in a product, which means that the product is not altered or damaged during the measurement.
In short, a water activity meter using the dew point measurement method offers great accuracy, fast data collection and a wide range of applications, making it an ideal option for the food industry and other industrial applications that require a reliable measurement of the quantity of free water.
The ideal aw meter for measuring the shelf life of freeze-dried and highly dehydrated products
aWLife, the free water (aw) meter designed and manufactured in Italy by Steroglass, is the solution for determining the shelf life of foods and pharmaceutical products.
The dew point measurement method makes it the most efficient water activity meter for measuring freeze-dried and highly dehydrated products.

